|
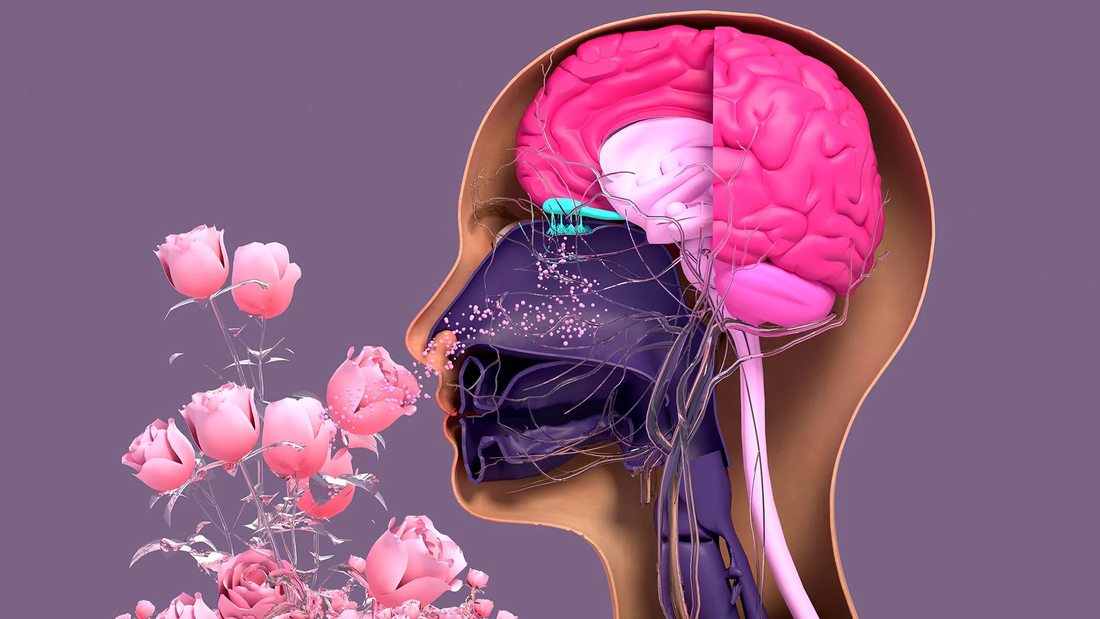
By Ana Elena Sastrias, Certified Olfaction Trainer and Certified Natural Perfumer Our Vision is the door to our Visual Reality. Our Sense of Smell completes that Visual Reality with the perception of Scents and Flavours, generating Memories and Emotions and Connections with other beings, including human beings. Human beings, as with some other animals including bacteria, have different perceptions of the Sense of Smell. Some animals have more complex sensory systems than others. As we evolved and became stewards of land and animals, we also developed Art, Culture and Science. We, as a species, wanted to separate from the other animals and other species, destroying that relationship we had in the beginning between animals and flora that had brought us together through the primary senses and instincts. We have also developed various lifestyles that have de-programmed our physiological priorities as a species, by alienating our Sense of Smell as almost unimportant, giving much more priority to other senses, such as Vision. Fragrances, being very ephemeral, are very quickly overwhelmed, replaced by sound and visual inputs. The sense of smell, ancestrally the First Sense, has become the last sense we use. During the last three decades, Humans have been seeking the state of wellbeing, re-educating ourselves to desire sustainability and health, developing the appreciation of natural products, while rejecting the use of synthetics. Still, a lot more needs to be done in this matter. Being aware of how our Olfactory system works can provide some insight and awareness of what to smell and how natural scent molecules can directly impact our health. In our present environment, after the Covid-19 pandemic, it seems that we have mostly lost our Olfactory sense and must re-learn to smell. Mask protection and lockouts affected our sense of perception of reality, blocking our free instinctive power to breath and lowering the capacity of the Olfactory Sense. Now that we are beginning to become free of masks, we need to re-train our sense of smell and our breathing techniques. From birth we connect with our mothers through the sense of smell. Our mothers when having us as babies, not only shared genes, but also shared phenotype features such as smells. Babies have a very fresh and well-developed sense of smell which guides them to receive messages that make them feel safe. The olfactory sense of babies is so sensitive that allows them to react to odours through motor reactions, respiratory and cardiac rhythmic changes. Babies less than two weeks old orient themselves automatically towards maternal odours. They learn to recognise their mother by her smell, which they will prefer to any other smell and will bond to it. It could be said that “newborns” see with their noses. People losing their olfactory sense, very often develop symptoms of depression and feel very isolated aside from having a great negative impact in their quality of life and a loss of their sense of safety. That is why it is so important to re-train our sense of smell through Olfaction Training, suitable for future perfumers, trained perfumers and people suffering from affected sense of smell like anosmia, hyposmia or dysosmia conditions. There is also a Health aspect associated with the correct way of using our sense of smell and our relationship with Nature. It is now paramount to protect our Natural Resources, our flora, woodlands, rivers, lakes, and oceans, as they provide us with scent molecules that can contribute positively to our health and even repair our DNA. We, as Humans, share DNA with other species. We can even repair our hormones and DNA by smelling scents from Nature, like flowers or plants, by using proper Breathing and Olfaction Techniques and using the Natural Raw Materials adequate for Natural Perfumery and Aromatherapy. The Beneficial Power of Nature Like many raw materials Opoponax, which means in Greek “heal everything,” is a resin which Dioscorides used to heal Nero in the times of The Roman Empire. This plant, native of Abyssinia, is also produced in China and sent to India which uses it for Religious purposes. The essential oil of Opoponax is obtained by distillation and it is an excellent fixative used in perfumery. Marjoram, since antiquity, has been used by Egyptians and Arabs to relieve migraine, and its scent has soothing and comforting qualities. It is generally used for calming anxiety, nervousness, migraine and insomnia and it is recommended for the people suffering from depression. Other raw materials, like Juniper, have antiseptic, depurative and diuretic properties. Geranium has anti-inflammatory properties. Eucalyptus can be used to treat fevers or as a decongestant of the respiratory tract. Cinnamon, since antiquity, is originally from Sri Lanka and can also be found in the Seychelles and Madagascar. is It is also used not just for culinary purposes, but for medicinal purposes from its stimulating, tonic properties and through improving blood circulation. Cinnamon can also be used as an antiseptic. Many of these and other natural plant raw materials have been used for a thousand years in many forms. Fumes, ointments, oils, and essential oils with purifying effects have been used for their restorative properties to our healthy electromagnetic vibration frequencies. Essential oils’ scent molecules travel to the nose receptors that detect the oil molecules with specific frequency, and then send signals of these vibrational frequencies to the brain. The intention of the healing process is to provide the correct vibrational frequency required that will bring the brain and body back to a state of coherence. This is the therapy by special vibration remedies capable of healing or rebalancing the brain’s and body’s DNA cells. That it is why is so important to smell raw materials from Nature and not from synthetic molecules, as the Natural scent molecules have all the complete vibrational frequency codes necessary to be used in healing. Synthetic scent molecules will not have the same healing power, would not be beneficial for treating health matters and, in the worst cases, may distort our hormones and DNA. The New Luxury Code
For these reasons, the International Perfume Foundation developed the “New Luxury Code” in Natural Perfumery products that allows us as perfumers to work on this goal by taking into consideration the meaning of “Luxury” as respectful, exceptional, sustainable, perfect, not necessarily expensive, smells and feels great, contributes to culture, sensitive to everyone’s culture, produces a change, makes us happy, and is eternally beautiful. The Natural Perfumery Teacher's Academy is proposing monthly online Olfaction Training Courses in French, English, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Chinese and Arabic languages.
2 Comments
|
Archives
March 2024
Categories
All
|
- Home
- About
- Why choosing us
- Mission
- Academicians
- IPF Certification
-
COURSES
-
MASTER CLASSES
- Teaching Methodology
- Natural Raw Material Extraction Methods >
- Natural Candle Making
- Healing Gardening
- Sustainable Oud MasterClass
- World Perfume History Master Class
- Scent Design and Formula Building >
- Fragrant Botany & Chemistry >
- Perfume Design, Concept and Storytelling
- French Natural Aromachology #1
- French Natural Aromachology #2
- Olfaction Training for Children
- Accords - Musks
- Accords - Chypre
- Accords - White Florals 1
- Accords - Fougeres and Aromatics
- FRAGRANCE DEVELOPMENT
- SPEAKERS
- EXHIBITIONS
- Partners
- Blog
- Contact







 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
